| |  |
Advertisement |  | Got Methods? Need More?
Download Tissue Dissociation Guide Free
The definitive manual for primary cell isolation, tissue dissociation and harvesting.
Select, develop, optimize protocols and better understand the process of enzymatic primary cell isolation and tissue dissociation.
Plus hundreds of new detailed references.
Try More? Free Collagenase Sample Program |  | | |  | | | | | Weekly Content Alert
|  | | 01 April 2015 |  | | Featured image: |  | 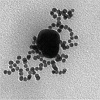 |  | | Schiller et al. present a protein-based approach for assembly of nanoparticles with defined interparticle distances. | | | | Advertisement | Nature Communications is now fully open access
All new submissions if accepted, will be published open access and an article processing charge will apply. For more information visit the website.
Visit our open access funding page or contact openaccess@nature.com to learn more on APC funding. | | | | | |  |
Advertisement |  | | |  | | | | | Latest Articles | View all Articles | | | | 
 
 
 | Immune complexes regulate bone metabolism through FcRγ signalling |  | | Takako Negishi-Koga, Hans-Jürgen Gober, Eriko Sumiya, Noriko Komatsu, Kazuo Okamoto, Shinichiro Sawa, Ayako Suematsu, Tomomi Suda, Kojiro Sato, Toshiyuki Takai and Hiroshi Takayanagi |  | | Bone and the immune system are functionally intertwined. This study shows that osteoclastogenesis is modulated by the intensity of Fcγ receptor signalling, which is shaped by the balance between the positive and negative Fcγ receptors expressed on osteoclasts and the availability of their ligands, immune complexes. |  | | 31 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7637 |  | | Biological Sciences Immunology Medical research | 
 
 
 | Triaminopyrimidine is a fast-killing and long-acting antimalarial clinical candidate OPEN |  | | Shahul Hameed P., Suresh Solapure, Vikas Patil, Philipp P. Henrich, Pamela A. Magistrado, Sowmya Bharath, Kannan Murugan, Pavithra Viswanath, Jayashree Puttur, Abhishek Srivastava, Eknath Bellale, Vijender Panduga, Gajanan Shanbag, Disha Awasthy, Sudhir Landge, Sapna Morayya, Krishna Koushik, Ramanatha Saralaya, Anandkumar Raichurkar, Nikhil Rautela et al. |  | | The emergence of resistant Plasmodium strains fuels the search for new antimalarials. Here, the authors present a new class of potent antimalarial compounds, the triaminopyrimidines, that display low toxicity and long half-life in animal models. |  | | 31 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7715 |  | | Biological Sciences Chemical biology Medicinal chemistry Microbiology | 
 | Structural basis for full-spectrum inhibition of translational functions on a tRNA synthetase OPEN |  | | Pengfei Fang, Xue Yu, Seung Jae Jeong, Adam Mirando, Kaige Chen, Xin Chen, Sunghoon Kim, Christopher S. Francklyn and Min Guo |  | | Borrelidin is an antibiotic with antimicrobial, antifungal, antimalarial and immunosuppressive activity that targets threonyl-tRNA synthetase. Here the authors show that borrelidin functions by preventing binding of all three ThrRS substrates and inducing a distinct, non-productive, conformation of the enzyme. |  | | 31 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7402 |  | | Biological Sciences Biochemistry Chemical biology | 
 | Genomic signatures of human and animal disease in the zoonotic pathogen Streptococcus suis OPEN |  | | Lucy A. Weinert, Roy R. Chaudhuri, Jinhong Wang, Sarah E. Peters, Jukka Corander, Thibaut Jombart, Abiyad Baig, Kate J. Howell, Minna Vehkala, Niko Välimäki, David Harris, Tran Thi Bich Chieu, Nguyen Van Vinh Chau, James Campbell, Constance Schultsz, Julian Parkhill, Stephen D. Bentley, Paul R. Langford, Andrew N. Rycroft, Brendan W. Wren et al. |  | | The bacterium Streptococcus suis causes respiratory tract infections in pigs and meningitis in humans. Here, the authors show that human disease isolates are limited to a single virulent population and find no consistent genomic differences between pig and human isolates. |  | | 31 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7740 |  | | Biological Sciences Evolution Genetics Microbiology | 
 | Glycopeptide analogues of PSGL-1 inhibit P-selectin in vitro and in vivo |  | | Venkata R. Krishnamurthy, Mohammed Y. R. Sardar, Yu Ying, Xuezheng Song, Carolyn Haller, Erbin Dai, Xiaocong Wang, Donny Hanjaya-Putra, Lijun Sun, Vasilios Morikis, Scott I. Simon, Robert J. Woods, Richard D. Cummings and Elliot L. Chaikof |  | | Inhibiting the interaction between the membrane protein P-selectin and its ligand PSGL-1 is thought to block inflammation. Here the authors report an efficient stereoselective synthesis for PSGL-1 glycopeptide mimics and show that these compounds inhibit PSGL-1/P-selectin in vitro and in vivo. |  | | 31 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7387 |  | | Biological Sciences Medical research Medicinal chemistry | 
 | Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss OPEN |  | | Ulrike Harre, Stefanie C. Lang, René Pfeifle, Yoann Rombouts, Sabine Frühbeißer, Khaled Amara, Holger Bang, Anja Lux, Carolien A. Koeleman, Wolfgang Baum, Katharina Dietel, Franziska Gröhn, Vivianne Malmström, Lars Klareskog, Gerhard Krönke, Roland Kocijan, Falk Nimmerjahn, René E. M. Toes, Martin Herrmann, Hans Ulrich Scherer et al. |  | | The IgG sugar moiety modulates the binding of immune complexes to their Fcγ receptors resulting in pro- or anti-inflammatory response. This study shows that IgG sialylation also affects osteoclastogenesis and bone mass in mice and humans, identifying a new link between bone and the immune system. |  | | 31 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7651 |  | | Biological Sciences Immunology Medical research | 
 
 
 
 | Identification of myopia-associated WNT7B polymorphisms provides insights into the mechanism underlying the development of myopia |  | | Masahiro Miyake, Kenji Yamashiro, Yasuharu Tabara, Kenji Suda, Satoshi Morooka, Hideo Nakanishi, Chiea-Chuen Khor, Peng Chen, Fan Qiao, Isao Nakata, Yumiko Akagi-Kurashige, Norimoto Gotoh, Akitaka Tsujikawa, Akira Meguro, Sentaro Kusuhara, Ozen Polasek, Caroline Hayward, Alan F. Wright, Harry Campbell, Andrea J. Richardson et al. |  | | Myopia is a significant and increasing public health concern. Here Miyake et al. conduct a genome-wide association study and identify WNT7B as a susceptibility gene across different ethnic groups, suggesting a possible role in the development of myopia. |  | | 31 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7689 |  | | Biological Sciences Genetics | 
 | Mechanical surface waves accompany action potential propagation |  | | Ahmed El Hady and Benjamin B. Machta |  | | Action potentials in neurons are accompanied by a mechanical displacement of the axonal membrane. Here, the authors present a model to describe these as surface waves which are driven by changes in charge separation, and compare their model to published experimental results from squid giant axons and garfish olfactory nerve bundles. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7697 |  | | Biological Sciences Biophysics | 
 | An allosteric photoredox catalyst inspired by photosynthetic machinery OPEN |  | | Alejo M. Lifschitz, Ryan M. Young, Jose Mendez-Arroyo, Charlotte L. Stern, C. Michael McGuirk, Michael R. Wasielewski and Chad A. Mirkin |  | | Photosynthetic systems regulate light harvesting via structural and electronic control of antenna proteins. Here, the authors report a light-harvesting antenna/reaction centre mimic that can be allosterically regulated using mild and redox-inactive inputs, via a coordination framework with hemilabile ligands. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7541 |  | | Chemical Sciences Catalysis Inorganic chemistry | 
 | Microtubule disruption synergizes with oncolytic virotherapy by inhibiting interferon translation and potentiating bystander killing |  | | Rozanne Arulanandam, Cory Batenchuk, Oliver Varette, Chadi Zakaria, Vanessa Garcia, Nicole E. Forbes, Colin Davis, Ramya Krishnan, Raunak Karmacharya, Julie Cox, Anisha Sinha, Andrew Babawy, Katherine Waite, Erica Weinstein, Theresa Falls, Andrew Chen, Jeff Hamill, Naomi De Silva, David P. Conrad, Harold Atkins et al. |  | | Microtubule-destabilizing drugs and oncolytic viruses are two unrelated approaches to battle cancer. Here the authors show that microtubule-destabilizing drugs potentiate the efficiency of oncolytic rhabdoviruses by altering the cytokine production and response of the tumour cells. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7410 |  | | Biological Sciences Cancer Cell biology Immunology | 
 | The nuclear translocation of ERK1/2 as an anticancer target |  | | Alexander Plotnikov, Karen Flores, Galia Maik-Rachline, Eldar Zehorai, Einat Kapri-Pardes, Denise A. Berti, Tamar Hanoch, Michal J. Besser and Rony Seger |  | | The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) cascade is involved in the induction and maintenance of cancers. Here the authors design an ERK-derived peptide that blocks ERK nuclear import, thus proposing a novel approach to treat tumours with mutational activation of the ERK pathway. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7685 |  | | Biological Sciences Cancer Cell biology | 
 | Human monoclonal antibodies targeting the haemagglutinin glycoprotein can neutralize H7N9 influenza virus |  | | Zhe Chen, Jianmin Wang, Linlin Bao, Li Guo, Weijia Zhang, Ying Xue, Hongli Zhou, Yan Xiao, Jianwei Wang, Fan Wu, Ying Deng, Chuan Qin and Qi Jin |  | | Treatment options for prevention and control of fatal H7N9 influenza infections remain limited. Here, the authors show that two human monoclonal antibodies protect mice against H7N9 strains when administered before or after H7N9 infection. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7714 |  | | Biological Sciences Immunology Microbiology Virology | 
 | The ancestral role of nodal signalling in breaking L/R symmetry in the vertebrate forebrain |  | | Ronan Lagadec, Laurent Laguerre, Arnaud Menuet, Anis Amara, Claire Rocancourt, Pierre Péricard, Benoît G. Godard, Maria Celina Rodicio, Isabel Rodriguez-Moldes, Hélène Mayeur, Quentin Rougemont, Sylvie Mazan and Agnès Boutet |  | | The epithalamus exhibits left-right asymmetries with different magnitudes among vertebrates. Here, the authors show that the catshark and two lampreys have conserved molecular asymmetries between the left and right developing epithalamus which are controlled by nodal signalling. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7686 |  | | Biological Sciences Developmental biology Evolution Genetics Zoology | 
 | Voltage-dependent gating of KCNH potassium channels lacking a covalent link between voltage-sensing and pore domains OPEN |  | | Éva Lörinczi, Juan Camilo Gómez-Posada, Pilar de la Peña, Adam P. Tomczak, Jorge Fernández-Trillo, Ulrike Leipscher, Walter Stühmer, Francisco Barros and Luis A. Pardo |  | | The pore of voltage-gated ion channels opens in response to membrane depolarization sensed by a separate voltage-sensing domain. Here, Lörinczi et al. show that, contrary to assumptions, no physical linker is required to transmit changes from the voltage-sensing to the permeation domain of KCNH channels. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7672 |  | | Biological Sciences Biophysics | 
 
 
 | Cmr1/WDR76 defines a nuclear genotoxic stress body linking genome integrity and protein quality control OPEN |  | | Irene Gallina, Camilla Colding, Peter Henriksen, Petra Beli, Kyosuke Nakamura, Judith Offman, David P. Mathiasen, Sonia Silva, Eva Hoffmann, Anja Groth, Chunaram Choudhary and Michael Lisby |  | | Defects in the DNA replication checkpoint can lead to genomic instability and cancer. Here the authors show that Cmr1/WDR76 participates in the DNA replication stress response and—along with several other components—defines a new cellular compartment that forms during cellular stress. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7533 |  | | Biological Sciences Cell biology Molecular biology | 
 | Bidecadal North Atlantic ocean circulation variability controlled by timing of volcanic eruptions |  | | Didier Swingedouw, Pablo Ortega, Juliette Mignot, Eric Guilyardi, Valérie Masson-Delmotte, Paul G. Butler, Myriam Khodri and Roland Séférian |  | | While present in palaeoclimate records, the drivers behind 20-year climate variability are poorly understood. Here, using climate simulations and in situ and palaeo data, the authors present a possible link between volcanic eruptions, Great Salinity Anomalies and the Atlantic overturning circulation. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7545 |  | | Earth Sciences Atmospheric science Climate science Oceanography | 
 | HIV-1 capsids bind and exploit the kinesin-1 adaptor FEZ1 for inward movement to the nucleus |  | | Viacheslav Malikov, Eveline Santos da Silva, Vladimir Jovasevic, Geoffrey Bennett, Daniel A. de Souza Aranha Vieira, Bianca Schulte, Felipe Diaz-Griffero, Derek Walsh and Mojgan H. Naghavi |  | | Many viruses take advantage of microtubule-dependent motor proteins to move through the cell. Malikov et al. show that HIV-1 recruits the kinesin-1 adaptor FEZ1, and that the opposing activities of kinesin-1 and dynein motors are both required for the transport of HIV-1 capsids towards the nucleus. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7660 |  | | Biological Sciences Cell biology Virology | 
 | Enriched environment reduces glioma growth through immune and non-immune mechanisms in mice OPEN |  | | Stefano Garofalo, Giuseppina D’Alessandro, Giuseppina Chece, Frederic Brau, Laura Maggi, Alessandro Rosa, Alessandra Porzia, Fabrizio Mainiero, Vincenzo Esposito, Clotilde Lauro, Giorgia Benigni, Giovanni Bernardini, Angela Santoni and Cristina Limatola |  | | Enriched environment is known to be beneficial in several disease settings. Here the authors show that mice pre-exposed to enriched environment survive longer when challenged with glioma due to increased antitumour immunity, and identify soluble factors that mediate these effects. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7623 |  | | Biological Sciences Cancer Immunology Neuroscience | 
 | Skp2–MacroH2A1–CDK8 axis orchestrates G2/M transition and tumorigenesis |  | | Dazhi Xu, Chien-Feng Li, Xian Zhang, Zhaohui Gong, Chia-Hsin Chan, Szu-Wei Lee, Guoxiang Jin, Abdol-Hossein Rezaeian, Fei Han, Jing Wang, Wei-Lei Yang, Zi-Zhen Feng, Wei Chen, Ching-Yuan Wu, Ying-Jan Wang, Lu-Ping Chow, Xiao-Feng Zhu, Yi-Xin Zeng and Hui-Kuan Lin |  | | Skp2 forms part of the SCF complex—an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Here the authors identify macroH2A1 as a novel target of Skp2 and propose an axis of regulation involving Skp2-macroH2A1-CDK8-p27 in cancer. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7641 |  | | Biological Sciences Cancer Molecular biology | 
 
 
 
 | Global migration of influenza A viruses in swine |  | | Martha I. Nelson, Cécile Viboud, Amy L. Vincent, Marie R. Culhane, Susan E. Detmer, David E. Wentworth, Andrew Rambaut, Marc A. Suchard, Edward C. Holmes and Philippe Lemey |  | | The 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic exposed major gaps in our knowledge of the spatial ecology and evolution of swine influenza A viruses. Here Nelson et al. perform an extensive phylogenetic analysis of these viruses and show that the global trade of live swine strongly predicts their spatial dissemination. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7696 |  | | Biological Sciences Ecology Evolution Virology | 
 | Suppressor of Deltex mediates Pez degradation and modulates Drosophila midgut homeostasis |  | | Chao Wang, Wenxiang Zhang, Meng-Xin Yin, Lianxin Hu, Peixue Li, Jiajun Xu, Hongling Huang, Shimin Wang, Yi Lu, Wenqing Wu, Margaret S. Ho, Lin Li, Yun Zhao and Lei Zhang |  | | The protein tyrosine phosphatase Pez controls intestinal stem cell proliferation in Drosophila by inhibiting the Hippo pathway transcription factor Yorkie. Wang et al. reveal that Pez protein stability is regulated by interactions with the E3 ubiquitin ligase Suppressor of Deltex. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7607 |  | | Biological Sciences Cell biology | 
 
 
 | Myeloid cell-derived inducible nitric oxide synthase suppresses M1 macrophage polarization OPEN |  | | Geming Lu, Ruihua Zhang, Shuo Geng, Liang Peng, Padmini Jayaraman, Chun Chen, Feifong Xu, Jianjun Yang, Qin Li, Hao Zheng, Kimberly Shen, Juan Wang, Xiyu Liu, Weidong Wang, Zihan Zheng, Chen-Feng Qi, Chuanping Si, John Cijiang He, Kebin Liu, Sergio A. Lira et al. |  | | In response to microbial ligands, IRF5 promotes pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage activation and production of nitrous oxide. Here the authors show that nitrous oxide modifies IRF5 tyrosine residues as a negative feedback, limiting the inflammatory response and protecting from endotoxin shock. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7676 |  | | Biological Sciences Immunology | 
 
 | Genome-wide profiling of p53-regulated enhancer RNAs uncovers a subset of enhancers controlled by a lncRNA OPEN |  | | Nicolas Léveillé, Carlos A. Melo, Koos Rooijers, Angel Díaz-Lagares, Sonia A. Melo, Gozde Korkmaz, Rui Lopes, Farhad Akbari Moqadam, Ana R. Maia, Patrick J. Wijchers, Geert Geeven, Monique L. den Boer, Raghu Kalluri, Wouter de Laat, Manel Esteller and Reuven Agami |  | | Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as important regulators of gene expression through several distinct mechanisms. Here the authors further delineate the role of p53-induced lncRNAs within the p53-responsive pathways through the activation of enhancers. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7520 |  | | Biological Sciences Bioinformatics Cancer Molecular biology | 
 | On the tear resistance of skin OPEN |  | | Wen Yang, Vincent R. Sherman, Bernd Gludovatz, Eric Schaible, Polite Stewart, Robert O. Ritchie and Marc A. Meyers |  | | It is known that skin has a large tear resistance, but little is known of the mechanism behind this. Here, the authors carry out a structural analysis of rabbit skin to show how the deformation of collagen fibrils in the skin results in a strong resistance to tear propagation. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7649 |  | | Biological Sciences Materials science | 
 | Ainsliadimer A selectively inhibits IKKα/β by covalently binding a conserved cysteine OPEN |  | | Ting Dong, Chao Li, Xing Wang, Longyang Dian, Xiuguo Zhang, Lin Li, She Chen, Ran Cao, Li Li, Niu Huang, Sudan He and Xiaoguang Lei |  | | IKK is a key inducer of NF-κB, and has been targeted by several small molecule drugs. Here the authors show that a natural product from a Chinese medical herb inhibits NF-κB via covalent binding to a unique conserved region of IKK, and efficiently inhibits tumour growth and sepsis in mice. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7522 |  | | Biological Sciences Cancer Chemical biology | 
 | Signatures of the Giant Pairing Vibration in the 14C and 15C atomic nuclei OPEN |  | | F. Cappuzzello, D. Carbone, M. Cavallaro, M. Bondì, C. Agodi, F. Azaiez, A. Bonaccorso, A. Cunsolo, L. Fortunato, A. Foti, S. Franchoo, E. Khan, R. Linares, J. Lubian, J. A. Scarpaci and A. Vitturi |  | | The Giant Pairing Vibration is a collective mode in an atomic nucleus caused by coherence between particle-particle excitations, which has so far eluded detection. Cappuzzello et al. present signatures for its existence via heavy-ion-induced two-neutron transfer reactions in carbon nuclei. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7743 |  | | Physical Sciences Atomic and molecular physics | 
 
 | ID4 controls mammary stem cells and marks breast cancers with a stem cell-like phenotype |  | | Simon Junankar, Laura A. Baker, Daniel L. Roden, Radhika Nair, Ben Elsworth, David Gallego-Ortega, Paul Lacaze, Aurélie Cazet, Iva Nikolic, Wee Siang Teo, Jessica Yang, Andrea McFarland, Kate Harvey, Matthew J. Naylor, Sunil R. Lakhani, Peter T. Simpson, Ashwini Raghavendra, Jodi Saunus, Jason Madore, Warren Kaplan et al. |  | | Basal-like breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease with poor prognosis; however, its cellular origins and aetiology are poorly understood. Here the authors provide evidence that ID4 is a key controller of mammary stem/progenitor cell self-renewal, acting upstream of Notch signalling to repress luminal fate commitment. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7548 |  | | Biological Sciences Cell biology Developmental biology | 
 
 
 
 
 | Giant oscillating thermopower at oxide interfaces OPEN |  | | Ilaria Pallecchi, Francesca Telesio, Danfeng Li, Alexandre Fête, Stefano Gariglio, Jean-Marc Triscone, Alessio Filippetti, Pietro Delugas, Vincenzo Fiorentini and Daniele Marré |  | | Electrons sitting in quantum wells at the interface between two oxides can localize in the disordered potential, completely changing their properties. Here, the authors observe unexpectedly large thermopower that oscillates upon carrier density modulation and ascribe it to strong electron-phonon coupling. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7678 |  | | Physical Sciences Materials science | 
 | Nanoscale determination of the mass enhancement factor in the lightly doped bulk insulator lead selenide OPEN |  | | Ilija Zeljkovic, Kane L. Scipioni, Daniel Walkup, Yoshinori Okada, Wenwen Zhou, R Sankar, Guoqing Chang, Yung Jui Wang, Hsin Lin, Arun Bansil, Fangcheng Chou, Ziqiang Wang and Vidya Madhavan |  | | Electron–phonon coupling influences the thermal and electronic properties of many solid materials. Zeljkovic et al. now combine Landau level spectroscopy and scanning tunnelling microscopy to extract quantitative information on electron–phonon coupling in the insulator lead selenide. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7559 |  | | Physical Sciences Condensed matter Materials science | 
 | Capturing the cloud of diversity reveals complexity and heterogeneity of MRSA carriage, infection and transmission OPEN |  | | Gavin K. Paterson, Ewan M. Harrison, Gemma G. R. Murray, John J. Welch, James H. Warland, Matthew T. G. Holden, Fiona J. E. Morgan, Xiaoliang Ba, Gerrit Koop, Simon R. Harris, Duncan J. Maskell, Sharon J. Peacock, Michael E. Herrtage, Julian Parkhill and Mark A. Holmes |  | | Populations of bacterial pathogens can be diverse within colonized individuals. Here, the authors sequence the genomes of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from staff and animal patients at a veterinary hospital and show considerable within-host diversity that can rise and fall over time. |  | | 27 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7560 |  | | Biological Sciences Evolution Medical research Microbiology | 
 | PD-1 alters T-cell metabolic reprogramming by inhibiting glycolysis and promoting lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation OPEN |  | | Nikolaos Patsoukis, Kankana Bardhan, Pranam Chatterjee, Duygu Sari, Bianling Liu, Lauren N. Bell, Edward D. Karoly, Gordon J. Freeman, Victoria Petkova, Pankaj Seth, Lequn Li and Vassiliki A. Boussiotis |  | | Activation of T cells results in metabolic reprogramming to favour glycolysis. Here, Patsoukis et al. show that the surface receptor PD-1 inhibits glycolysis and increases the metabolism of lipids, providing a potential mechanism for the blockade of T effector functions but also for the longevity accompanying T cell exhaustion. |  | | 26 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7692 |  | | Biological Sciences Cell biology Immunology | 
 
 | Magnetoelectric quasi-(0-3) nanocomposite heterostructures |  | | Yanxi Li, Zhongchang Wang, Jianjun Yao, Tiannan Yang, Zhiguang Wang, Jia-Mian Hu, Chunlin Chen, Rong Sun, Zhipeng Tian, Jiefang Li, Long-Qing Chen and Dwight Viehland |  | | Magnetoelectric composites of magnetic and ferroelectric components are promising for their use in applications such as information storage. Here, the authors find that magnetic quasiparticles embedded in a ferroelectric film matrix show promising properties compared to the usual thin-film architectures. |  | | 26 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7680 |  | | Physical Sciences Condensed matter Materials science | 
 
 
 | Mitochondrial protein import receptors in Kinetoplastids reveal convergent evolution over large phylogenetic distances OPEN |  | | Jan Mani, Silvia Desy, Moritz Niemann, Astrid Chanfon, Silke Oeljeklaus, Mascha Pusnik, Oliver Schmidt, Carolin Gerbeth, Chris Meisinger, Bettina Warscheid and André Schneider |  | | Protein translocation into the mitochondrion is a conserved process in all eukaryotes. Here, Mani et al. describe a non-conventional translocase complex in Trypanosoma brucei and propose that protein import receptors were recruited to the core complex after the divergence of the major eukaryotic supergroups. |  | | 26 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7646 |  | | Biological Sciences Biochemistry Evolution | 
 
 
 | The transcription factor Foxc1 is necessary for Ihh–Gli2-regulated endochondral ossification |  | | Michiko Yoshida, Kenji Hata, Rikako Takashima, Koichiro Ono, Eriko Nakamura, Yoshifumi Takahata, Tomohiko Murakami, Sachiko Iseki, Teruko Takano-Yamamoto, Riko Nishimura and Toshiyuki Yoneda |  | | Skeletal development relies on endochondral ossification. Here the authors show that transcription factors Foxc1 and Gli2 interact to modulate expression of Ihh target genes that control endochondral ossification, and that disruption of this interaction partly underlies skeletal disorders in the Axenfeld–Rieger syndrome. |  | | 26 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7653 |  | | Biological Sciences Developmental biology Medical research | 
 | Ternary metal fluorides as high-energy cathodes with low cycling hysteresis OPEN |  | | Feng Wang, Sung-Wook Kim, Dong-Hwa Seo, Kisuk Kang, Liping Wang, Dong Su, John J. Vajo, John Wang and Jason Graetz |  | | Transition metal fluorides have high theoretical specific capacities as cathodes for lithium ion batteries, but low working potentials and poor energy efficiency limit their practical applications. Here, the authors report a group of ternary metal fluorides, which may overcome these problems. |  | | 26 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7668 |  | | Chemical Sciences Materials science Physical chemistry | 
 
 | EphrinB2 controls vessel pruning through STAT1-JNK3 signalling |  | | Ombretta Salvucci, Hidetaka Ohnuki, Dragan Maric, Xu Hou, Xuri Li, Sung Ok Yoon, Marta Segarra, Charles G. Eberhart, Amparo Acker-Palmer and Giovanna Tosato |  | | Pruning of newly formed blood vessels is an important and yet poorly understood aspect of angiogenesis. Here the authors show that endothelial phosphotyrosine-dependent EphrinB2 signalling represses JNK3 function via STAT1, and identify JNK3 as an effector of endothelial cell death and vessel pruning in mice. |  | | 26 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7576 |  | | Biological Sciences Cell biology Developmental biology | 
 | Aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis contributes to epilepsy and associated cognitive decline OPEN |  | | Kyung-Ok Cho, Zane R. Lybrand, Naoki Ito, Rebecca Brulet, Farrah Tafacory, Ling Zhang, Levi Good, Kerstin Ure, Steven G. Kernie, Shari G. Birnbaum, Helen E. Scharfman, Amelia J. Eisch and Jenny Hsieh |  | | Aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis often occurs after acute seizures that produce epilepsy and cognitive impairment but the role of neurogenesis in the development of epilepsy is unclear. Here the authors suppress adult neurogenesis in mice preceding seizures and show that it reduces subsequent chronic seizure frequency and epilepsy-associated cognitive decline. |  | | 26 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7606 |  | | Biological Sciences Neuroscience | 
 
 
 
 | Ti-substituted tunnel-type Na0.44MnO2 oxide as a negative electrode for aqueous sodium-ion batteries |  | | Yuesheng Wang, Jue Liu, Byungju Lee, Ruimin Qiao, Zhenzhong Yang, Shuyin Xu, Xiqian Yu, Lin Gu, Yong-Sheng Hu, Wanli Yang, Kisuk Kang, Hong Li, Xiao-Qing Yang, Liquan Chen and Xuejie Huang |  | | Aqueous sodium-ion batteries could be a potential solution for large-scale energy storage, but the conventional negative electrodes are not efficient. Here, the authors report a titanium-substituted tunnel-type Na0.44MnO2 material as a promising negative electrode for aqueous sodium-ion batteries. |  | | 25 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7401 |  | | Chemical Sciences Materials science Physical chemistry | 
 | Trained immunity in newborn infants of HBV-infected mothers OPEN |  | | Michelle Hong, Elena Sandalova, Diana Low, Adam J. Gehring, Stefania Fieni, Barbara Amadei, Simonetta Urbani, Yap-Seng Chong, Ernesto Guccione and Antonio Bertoletti |  | | The ability to fight infections matures after birth and is thus termed ‘trained immunity’. Here the authors show that cord blood cells from hepatitis B virus-infected mothers respond more strongly to bacterial infections, suggesting that viral exposure in utero promotes trained immunity in newborns. |  | | 25 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7588 |  | | Biological Sciences Immunology Medical research | 
 
 | Subsistence strategies in traditional societies distinguish gut microbiomes OPEN |  | | Alexandra J. Obregon-Tito, Raul Y. Tito, Jessica Metcalf, Krithivasan Sankaranarayanan, Jose C. Clemente, Luke K. Ursell, Zhenjiang Zech Xu, Will Van Treuren, Rob Knight, Patrick M. Gaffney, Paul Spicer, Paul Lawson, Luis Marin-Reyes, Omar Trujillo-Villarroel, Morris Foster, Emilio Guija-Poma, Luzmila Troncoso-Corzo, Christina Warinner, Andrew T. Ozga and Cecil M. Lewis et al. |  | | The gut microbiomes of urban-industrialized societies differ from those of traditional rural societies and hunter-gatherers. Here the authors perform a comparative analysis of available and new gut microbiome data to provide fresh insight into these differences. |  | | 25 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7505 |  | | Biological Sciences Ecology Microbiology | 
 | Multi-spectral fluorescent reporter influenza viruses (Color-flu) as powerful tools for in vivo studies OPEN |  | | Satoshi Fukuyama, Hiroaki Katsura, Dongming Zhao, Makoto Ozawa, Tomomi Ando, Jason E. Shoemaker, Izumi Ishikawa, Shinya Yamada, Gabriele Neumann, Shinji Watanabe, Hiroaki Kitano and Yoshihiro Kawaoka |  | | Animal models are important to study organismal immune responses to infection with influenza viruses. Here, Fukuyama et al. report a new generation of fluorescently labelled influenza viruses that facilitate the study of viral infections in animal models at cellular level. |  | | 25 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7600 |  | | Biological Sciences Immunology Microbiology Virology | 
 
 
 
 
 | |  | | |  | | | | | Latest Corrigenda | | | | |  | Corrigendum: Novel loci affecting iron homeostasis and their effects in individuals at risk for hemochromatosis |  | | Beben Benyamin, Tonu Esko, Janina S. Ried, Aparna Radhakrishnan, Sita H. Vermeulen, Michela Traglia, Martin Gögele, Denise Anderson, Linda Broer, Clara Podmore, Jiańan Luan, Zoltan Kutalik, Serena Sanna, Peter van der Meer, Toshiko Tanaka, Fudi Wang, Harm-Jan Westra, Lude Franke, Evelin Mihailov, Lili Milani et al. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7542 |  | | Biological Sciences Genetics Medical research | 
 | | | |  
 | | | |  | Corrigendum: New loci and coding variants confer risk for age-related macular degeneration in East Asians |  | | Ching-Yu Cheng, Kenji Yamashiro, Li Jia Chen, Jeeyun Ahn, Lulin Huang, Lvzhen Huang, Chui Ming G. Cheung, Masahiro Miyake, Peter D. Cackett, Ian Y. Yeo, Augustinus Laude, Ranjana Mathur, Junxiong Pang, Kar Seng Sim, Adrian H. Koh, Peng Chen, Shu Yen Lee, Doric Wong, Choi Mun Chan, Boon Kwang Loh et al. |  | | 30 March 2015 | doi: 10.1038/ncomms7817 |  | | Biological Sciences Genetics | 
 | | | |  | |  | | |  |  |  |  |  |  | Natureevents is a fully searchable, multi-disciplinary database designed to maximise exposure for events organisers. The contents of the Natureevents Directory are now live. The digital version is available here.
Find the latest scientific conferences, courses, meetings and symposia on natureevents.com. For event advertising opportunities across the Nature Publishing Group portfolio please contact natureevents@nature.com |  |  |  |  |  | |  | You have been sent this Table of Contents Alert because you have opted in to receive it. You can change or discontinue your e-mail alerts at any time, by modifying your preferences on your nature.com account at:www.nature.com/myaccount
(You will need to log in to be recognised as a nature.com registrant)
For further technical assistance, please contact our registration department
For other enquiries, please contact our customer feedback department
Nature Publishing Group | 75 Varick Street, 9th Floor | New York | NY 10013-1917 | USA
Nature Publishing Group's worldwide offices:
London - Paris - Munich - New Delhi - Tokyo - Melbourne
San Diego - San Francisco - Washington - New York - Boston
Macmillan Publishers Limited is a company incorporated in England and Wales under company number 785998 and whose registered office is located at Brunel Road, Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire RG21 6XS.
© 2013 Nature Publishing Group, a division of Macmillan Publishers Limited. All Rights Reserved. |  | | | |
No comments:
Post a Comment