Dear Reader ,
Be an ACS Industry Insider: https://connect.acspubs.org/Insider?LS=SciX
Sign-up and get free, monthly access to articles that cover exciting, cutting edge discoveries in Energy, Environmental Science and Agriculture.
Here is your customized Science X Newsletter for December 24, 2019:
Spotlight Stories Headlines
Astronomy & Space news
 | LAMOST first data release provides fundamental parameters of nearly 30,000 M dwarfsBased on the first data release (DR1) from the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST), astronomers have derived fundamental parameters of nearly 30,000 M-dwarf stars. The research paper presenting the findings was published December 13 on the arXiv pre-print repository. |
 | Astronomers describe a violent black hole outburst that provides new insight into galaxy cluster evolutionBillions of years ago, in the center of a galaxy cluster far, far away (15 billion light-years, to be exact), a black hole spewed out jets of plasma. As the plasma rushed out of the black hole, it pushed away material, creating two large cavities 180 degrees from each other. In the same way you can calculate the energy of an asteroid impact by the size of its crater, Michael Calzadilla, a graduate student at the MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research (MKI), used the size of these cavities to figure out the power of the black hole's outburst. |
 | Researchers make new discoveries set to reveal the geology of planets outside our solar systemThree OU astronomers today announced groundbreaking discoveries allowing scientists to understand planets outside the solar system. Professor Carole Haswell, Dr. Daniel Staab and Dr. John Barnes discovered three, new, nearby planetary systems. |
 | Our favorite holiday gift? A box of Apollo moon soilFortunately for today's scientists, Apollo-era leaders had the foresight to save much of the 842 pounds (382 kilograms) of Moon soil and rocks retrieved by NASA astronauts 50 years ago for future generations. They figured new crops of scientists, using instruments of their time, would be able to probe the samples with unprecedented rigor. |
 | The citizen scientists who helped map BennuWhen NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission spacecraft arrived at the asteroid Bennu, it discovered more rocks and boulders than envisioned. Mapping all these potential hazards was necessary to select a location to collect a sample of the surface for return to Earth. This effort was the work of multiple teams around the globe. One of those teams consisted of more than 3,500 citizen scientists who used CosmoQuest's Bennu Mappers project to mark rocks, measure boulders, and map craters. Together, they made more than 14 million annotations of features on a global map of Bennu. CosmoQuest is a project that is based at the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Ariz. (CosmoQuest.org). |
Technology news
 | AD-EYE: A co-simulation platform to verify functional safety concepts (FSCs) in self-driving vehiclesOver the past few years, a growing number of researchers and companies worldwide have been developing techniques for automated driving. Before self-driving vehicles can be introduced on real roads, however, their efficiency and safety will need to be ascertained. |
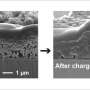 | High-performance anode for all-solid-state lithium batteries is made of silicon nanoparticlesA new study led by NIMS researchers reveals that in solid electrolytes, a silicon anode composed only of commercial silicon nanoparticles prepared by spray deposition exhibits excellent electrode performance, which has previously been observed only for film electrodes prepared by evaporation processes. The method is a cost-effective, atmospheric technique, and his new result therefore suggests that a low-cost and large-scale production of high-capacity anodes for use in all-solid-state lithium batteries is possible. |
 | How technology made us bid farewell to privacy in the last decadeIn 2011, Apple unveiled its first iPhone with artificial intelligence, a personal assistant named Siri that could answer questions and help keep track of our daily lives. |
 | Uber co-founder Travis Kalanick severs last ties to companyAbout decade after co-founding Uber, Travis Kalanick on Tuesday severed his last ties from the ride-hailing giant, announcing he would exit the board of directors at the end of 2019. |
 | Boeing document dump shows 'disturbing' picture on 737 MAX: officialBoeing provided a fresh batch of incriminating documents on the 737 MAX to regulators and congressional investigators, only hours after announcing a leadership shakeup, officials confirmed Tuesday. |
Medicine & Health news
 | Cellular culprit suspected of pushing dengue fever from bad to worse is cleared by transcriptsNo one knows what makes a mild dengue viral infection morph into a severe and sometimes deadly dengue hemorrhagic fever/dengue shock syndrome. Experts previously believed the likely cause was ramped up activity of T cells, which can massively boost an immune response to a virus. Now, however, researchers at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI), have found definitive evidence that CD4 T cells, one of two main subtypes of T cells, are not to blame. |
 | A molecular map of the brain's decision-making areaResearchers at Karolinska Institutet have come one step closer toward understanding how the part of our brain that is central for decision-making and the development of addiction is organized on a molecular level. In mouse models and with methods used for mapping cell types and brain tissue, the researchers were able to visualize the organization of different opioid-islands in striatum. Their spatiomolecular map, published in the journal Cell Reports, may further our understanding of the brain's reward-system. |
 | New technology allows control of gene therapy dosesScientists at Scripps Research in Jupiter have developed a special molecular switch that could be embedded into gene therapies to allow doctors to control dosing. |
 | Why isn't there a vaccine for staph?Staph bacteria, the leading cause of potentially dangerous skin infections, are most feared for the drug-resistant strains that have become a serious threat to public health. Attempts to develop a vaccine against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) have failed to outsmart the superbug's ubiquity and adaptability to antibiotics. |
 | Enrollment in Affordable Care Act holds steady for third straight yearEnrollment in Affordable Care Act coverage for next year has surpassed 8 million, a sign that many Americans still turn to the government health insurance program to help pay for their medical care. |
 | Report estimates readmission, death after vaping illness dischargeThe prevalence of rehospitalization and death after electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use-associated lung injury (EVALI) has been determined, and guidelines have been developed based on these findings. Both reports were published in the Dec. 20 early-release issue of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. |
 | Hate exercise? Small increases in physical activity can make a big differenceA new year typically brings new resolutions. While making resolutions is easy, sticking with them is not. Exercise-related resolutions consistently make the top 10 list, but up to 80% of resolutions to be healthier, including promises to exercise more, are tossed aside by February. |
 | ADA releases 2020 standards of medical care in diabetesA strong recurring message of individualizing patient care is echoed throughout the American Diabetes Association's Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020 published recently. Based on the latest scientific diabetes research and clinical trials, the Standards of Care includes new and updated recommendations and guidelines for caring for people with diabetes, including individualized recommendations for treatment of cardiovascular disease based on patients' pre-existing conditions, special considerations for older adults with type 1 diabetes, and revised recommendations and additional supporting evidence for use of rapidly changing diabetes technology. |
 | Research-based tips for sticking with your New Year's resolutionsHumans have a long history of making New Year's resolutions. The Babylonians are believed to be among the first to have set them more than 4,000 years ago. When Julius Caesar was emperor circa 46 B.C., the Romans had their own practice of offering sacrifices to Janus, the god of beginnings and endings, as they looked forward to each new year. |
 | How to support children whose parent works away for long periodsIt's not always possible for families to be together during the Christmas holidays if one parent is working away for several days. They could be on a tour of duty for the Australian Defence Force or in a fly-in, fly-out mining position. |
 | Global evaluation of lifestyle risk factors in teens: 1 in 3 at riskThe largest global investigation of the major lifestyle risk factors for non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in adolescents has been undertaken in a study led by University of Queensland researchers. |
 | Many younger patients with stomach cancer have a distinct disease, research discoversMany people under 60 who develop stomach cancer have a "genetically and clinically distinct" disease, new Mayo Clinic research has discovered. Compared to stomach cancer in older adults, this new, early onset form often grows and spreads more quickly, has a worse prognosis, and is more resistant to traditional chemotherapy treatments, the study finds. The research was published recently in the journal Surgery. |
 | How to stay fit when you're traveling for work or fun(HealthDay)—If you travel a lot for business or pleasure, you may think that the most exercise possible is lugging your bags in and out of a car or through an airport. But it's important to get in real exercise even when you're away from home. |
 | 'Shopping addiction' can cause harm, and it's moved online(HealthDay)—The holidays are peak buying time, and perhaps the worst time of the year for people who simply can't control their urge to shop. |
 | 12 million U.S. residents drove under influence of marijuana in 2018(HealthDay)—In 2018, 12 million U.S. residents reported driving under the influence of marijuana in the previous 12 months, according to research published in the Dec. 20 issue of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. |
 | Vitamin E acetate ID'd in lungs of most vaping illness patients(HealthDay)—Vitamin E acetate was identified in almost all patients with electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use-associated lung injury (EVALI), and there has been a decrease in EVALI cases since a peak in September 2019, according to a study and a report published online Dec. 20 in the New England Journal of Medicine. |
 | Could your indigestion be GERD?(HealthDay)—Heartburn. Millions of people suffer from it. But what exactly is it and, most important, could it actually be something serious? |
 | Acupuncture, acupressure may help cancer patients control pain(HealthDay)—The use of acupuncture and/or acupressure is associated with reduced cancer pain and decreased use of analgesics, according to a review published online Dec. 19 in JAMA Oncology. |
 | U.S. incidence of thyroid cancer plateaued in 2009(HealthDay)—From 2009 to 2016, the incidence of thyroid cancer reached a plateau and possibly started to decline, according to a research letter published in the Dec. 24/31 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association. |
Biology news
 | Mouse pups born from eggs derived from the granulosa cells that surround oocytesBy introducing a chemical cocktail to granulosa cells, researchers in China induced the cells to transform into functional oocytes in mice. Once fertilized, these oocytes were then successfully able to produce healthy offspring, showing no differences from naturally bred mice. The chemical reprogramming method appears December 24 in the journal Cell Reports. |
 | Chimpanzees spontaneously dance to musicA pair of researchers at Kyoto University has found that chimpanzees will spontaneously dance to music. In their paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Yuko Hattori and Masaki Tomonaga describe observing spontaneous dancing in chimps and how one chimp behaved when tested on dancing tendencies. |
 | Bee gut microbes have a division of labor when it comes to metabolizing complex polysaccharidesHoney bees are invaluable pollinators—cupids of the plant world facilitating the remixing of genes in the next generation of flowering vegetation. In return for their services, bees eat plant nectar and pollen. Nectar is an easily absorbable solution of sugars. But pollen contains plant cell walls, which have complex, branching chains of polysaccharides called pectin and hemicellulose. While these two polysaccharides can yield sugar monomers, it's only with the aid of specialized bacterial enzymes. Honey bees rely on their gut microbiota to produce these enzymes to break down polysaccharides. But scientists have wondered exactly how the microbial community carries out its helpful metabolism: who's responsible for what biochemical processes? |
 | Educational video could improve the welfare of millions of broiler chickensThe welfare of millions of broiler chickens could be improved thanks to an educational video to help farmers identify and encourage positive welfare in broilers. The video has been created following collaborative work by The Co-op, their chicken supplier, Two Sisters Food Group, and research partners the University of Bristol and FAI Farms. |
 | How cells relieve DNA replication stressDNA stores all of the information necessary for life phenomena, and a cell transmits its own genetic information to two daughter cells through DNA replication and cell division. Replication stress can be caused by extracellular and intracellular sources during DNA replication, which leads to slowed or stalled replication. If cells do not properly cope with such risks, chromosome break and rearrangement will occur, resulting in genomic instability. That helps explain why replication stress is one of the major contributors to cancer development. |
 | Expanding virophage diversityVirophages are small viruses with double-stranded DNA genomes that co-infect eukaryotic cells along with giant viruses. Almost all known virophage genomes share only four genes in common: major and minor capsid proteins (MCP and mCP, respectively), ATPase involved in DNA packaging, and PRO, a cysteine protease involved in capsid maturation. |
 | Vietnam seizes two tonnes of ivory and pangolin scalesVietnam seized more than two tonnes of ivory tusks and pangolin scales hidden inside wooden boxes shipped from Nigeria, state media reported Tuesday. |
This email is a free service of Science X Network
You received this email because you subscribed to our list.
If you do not wish to receive such emails in the future, please unsubscribe here.
You are subscribed as jmabs1@gmail.com. You may manage your subscription options from your Science X profile
No comments:
Post a Comment