TABLE OF CONTENTS
| March 2013 Volume 5, Issue 3 |  |  |  |  |  Thesis Thesis
 Books and Arts Books and Arts
 Research Highlights Research Highlights
 Blogroll Blogroll
 News and Views News and Views
 Review Review
 Articles Articles
 In Your Element In Your Element
| |  | |  |  | | Advertisement |  | New Nature Journals iPad app
Read Nature anytime, anywhere. Subscribe to Nature on the iPad for only $35.99
Download the new app from the app store.
*Apple exchange rates apply to international prices. |
|  | | | Thesis |  Top Top |  |  |  | Tangible assets pp147 - 148
Michelle Francl
doi:10.1038/nchem.1585
Michelle Francl argues we should embrace molecular models, not tuck them away in the closet.
|  | Books and Arts |  Top Top |  |  |  | Television: Chemistry at Christmas p149
Jamie Gallagher
doi:10.1038/nchem.1579
|  | Research Highlights |  Top Top |  |  |  | Ion-mobility spectroscopy: Crowning achievement | RNA cleavage: A radical solution | Ancient medicine: Two-millennia-old tablets | Biocatalysis: Promiscuous by nature
| Blogroll |  Top Top |  |  |  | Blogroll: It's time to talk p151
JessTheChemist
doi:10.1038/nchem.1584
|  | News and Views |  Top Top |  |  |  | |  | Review |  Top Top |  |  |  | Inhibition of α-helix-mediated protein-protein interactions using designed molecules pp161 - 173
Valeria Azzarito, Kérya Long, Natasha S. Murphy and Andrew J. Wilson
doi:10.1038/nchem.1568

α-Helix-mediated protein-protein interactions (PPIs) play a key role in the development of numerous infection and disease states. Modulating such interactions offers considerable therapeutic potential, however, identifying suitable inhibitors has proved challenging. This Review highlights recent and generic approaches for designing inhibitors of helix-mediated PPIs.
|  | Articles |  Top Top |  |  |  | Snapshot of the equilibrium dynamics of a drug bound to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase pp174 - 181
Daniel G. Kuroda, Joseph D. Bauman, J. Reddy Challa, Disha Patel, Thomas Troxler, Kalyan Das, Eddy Arnold and Robin M. Hochstrasser
doi:10.1038/nchem.1559

Conformational changes are known to occur during binding of the anti-AIDS drug rilpivirine to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, an essential enzyme for the replication of HIV. Vibrational spectroscopy, X-ray crystallography and simulations now show that water molecules play an essential role in this binding process, which may help it retain potency despite mutations within the binding pocket.
See also: News and Views by Cheatum
|  |  |  | Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells pp182 - 186
Giulia Biffi, David Tannahill, John McCafferty and Shankar Balasubramanian
doi:10.1038/nchem.1548

A structure-specific antibody generated and employed to visualize DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells shows that these structures are modulated during the cell cycle and can be stabilized by a small-molecule ligand. This provides substantive evidence for endogenous DNA G-quadruplex formation in mammalian cells.
See also: News and Views by Siddiqui-Jain & Hurley
|  |  |  | Charged and metallic molecular monolayers through surface-induced aromatic stabilization pp187 - 194
G. Heimel, S. Duhm, I. Salzmann, A. Gerlach, A. Strozecka, J. Niederhausen, C. Bürker, T. Hosokai, I. Fernandez-Torrente, G. Schulze, S. Winkler, A. Wilke, R. Schlesinger, J. Frisch, B. Bröker, A. Vollmer, B. Detlefs, J. Pflaum, S. Kera, K. J. Franke, N. Ueno, J. I. Pascual, F. Schreiber and N. Koch
doi:10.1038/nchem.1572

When monolayers of π-conjugated organic semiconductors interact with metal surfaces, most remain semiconducting. In some cases, however, the metallic character of the substrate is seen to extend onto the molecules. A mechanism for this intriguing phenomenon is now suggested and new strategies for chemical surface engineering are proposed.
|  |  |  | A ring-distortion strategy to construct stereochemically complex and structurally diverse compounds from natural products pp195 - 202
Robert W. Huigens III, Karen C. Morrison, Robert W. Hicklin, Timothy A. Flood Jr, Michelle F. Richter and Paul J. Hergenrother
doi:10.1038/nchem.1549

An approach for the construction of complex and diverse compound libraries is described, whereby natural products are altered through a series of ring system distortion reactions. The compounds produced have markedly different physiochemical properties from those in standard screening collections and thus could offer advantages in the search for lead molecules that can be developed into drug candidates.
Chemical compounds
See also: News and Views by Sharma & Tan
|  |  |  | A spray-drying strategy for synthesis of nanoscale metal–organic frameworks and their assembly into hollow superstructures pp203 - 211
Arnau Carné-Sánchez, Inhar Imaz, Mary Cano-Sarabia and Daniel Maspoch
doi:10.1038/nchem.1569

Metal–organic framework (MOF) nanoparticles and their assembly into three-dimensional superstructures are attracting attention in various fields. Now, a general spray-drying method has been developed to create more complex hollow spherical MOF superstructures and entrap guest species within them, thereby providing new routes to capsules, reactors and composite materials.
|  |  |  | Volume-conserving trans–cis isomerization pathways in photoactive yellow protein visualized by picosecond X-ray crystallography pp212 - 220
Yang Ouk Jung, Jae Hyuk Lee, Joonghan Kim, Marius Schmidt, Keith Moffat, Vukica Šrajer and Hyotcherl Ihee
doi:10.1038/nchem.1565

Time-resolved X-ray crystallography on photoactive yellow protein shows the existence of a short-lived, highly distorted intermediate whose reaction trajectory bifurcates along ‘bicycle-pedal’ and ‘hula-twist’ pathways. The bifurcating reaction pathways can be controlled by weakening the hydrogen bond between the chromophore and an adjacent residue, which switches off the bicycle-pedal pathway.
|  |  |  | A heparin-mimicking polymer conjugate stabilizes basic fibroblast growth factor pp221 - 227
Thi H. Nguyen, Sung-Hye Kim, Caitlin G. Decker, Darice Y. Wong, Joseph A. Loo and Heather D. Maynard
doi:10.1038/nchem.1573

Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is crucial for a range of diverse cellular processes, from wound healing to bone regeneration, yet is inherently unstable. This important biologic has now been covalently linked to a polymer that mimics the polysaccharide heparin to produce a conjugate that shows remarkable stability to a wide range of therapeutically and environmentally relevant stressors.
|  |  |  | An iron complex with pendent amines as a molecular electrocatalyst for oxidation of hydrogen pp228 - 233
Tianbiao Liu, Daniel L. DuBois and R. Morris Bullock
doi:10.1038/nchem.1571

Electricity can be produced by the oxidation of hydrogen in fuel cells, but the best catalyst for this is platinum, a precious metal of low abundance. Now a molecular complex of iron, a very abundant, inexpensive metal, has been rationally designed for the oxidation of H2 at room temperature.
Chemical compounds
|  |  |  | Molecular tweezers modulate 14-3-3 protein–protein interactions pp234 - 239
David Bier, Rolf Rose, Kenny Bravo-Rodriguez, Maria Bartel, Juan Manuel Ramirez-Anguita, Som Dutt, Constanze Wilch, Frank-Gerrit Klärner, Elsa Sanchez-Garcia, Thomas Schrader and Christian Ottmann
doi:10.1038/nchem.1570

A molecular tweezer has been shown to bind to the surface of a 14-3-3 protein through a particular lysine residue. This interaction — characterized in detail by protein crystallography and computational modelling — disrupts the protein's binding with partner proteins. These findings ascertain supramolecular chemistry as an enticing tool in chemical biology, here towards modulating protein functions.
|  |  |  | Phase-transfer-catalysed asymmetric synthesis of tetrasubstituted allenes pp240 - 244
Takuya Hashimoto, Kazuki Sakata, Fumiko Tamakuni, Mark J. Dutton and Keiji Maruoka
doi:10.1038/nchem.1567
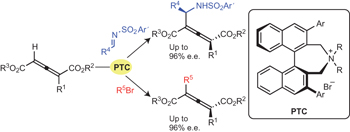
Substituted allenes with axial chirality are of great utility in organic chemistry owing to their unique structure and reactivity, but synthetic methods to access them are limited. Here, a catalytic asymmetric synthesis of tetrasubstituted allenes is described that builds on the use of phase-transfer-catalysed asymmetric functionalization of 1-alkylallene-1,3-dicarboxylates.
Chemical compounds
|  | In Your Element |  Top Top |  |  |  | Enigmatic astatine p246
D. Scott Wilbur
doi:10.1038/nchem.1580
D. Scott Wilbur points out the difficulty in studying the transient element astatine, and the need to understand its basic chemical nature to help in the development of targeted radiotherapy agents.
|  |  Top Top |  |  |  | | Advertisement |  | Subscribe to Nature Chemistry
Make sure you receive your own personal copy of Nature Chemistry. Your personal subscription gives you either 12 or 24 monthly print issues plus online access to the journal for 12 or 24 months.
- subscribe online here today |
|  | | |  |  |  |  |  |  | Natureevents is a fully searchable, multi-disciplinary database designed to maximise exposure for events organisers. The contents of the Natureevents Directory are now live. The digital version is available here.
Find the latest scientific conferences, courses, meetings and symposia on natureevents.com. For event advertising opportunities across the Nature Publishing Group portfolio please contact natureevents@nature.com |  |  |  |  |  |
|  |
|
|


No comments:
Post a Comment