Advertisement |
 |
Looking to keep pace with global news and research in the chemical sciences? Join RSC e-membership today to receive a digital subscription to Chemistry World, the unrivalled monthly magazine with a readership of 49,000. Access the latest developments in research and government policy, business news, features and opinion columns, jobs board, and networking opportunities. |  |
|
 |
 |
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
September 2012 Volume 4, Issue 9 |
 |  |  |
 |  Thesis Thesis
 Research Highlights Research Highlights
 Blogroll Blogroll
 News and Views News and Views
 Perspective Perspective
 Articles Articles
 In Your Element In Your Element
| |
 |
|
 |
 |
| Advertisement |
 |
Nature Insight: Chemistry and Energy
This Insight focuses on the developments in solar energy, water-based methods of electricity generation and the production of biofuels.
Access the Insight free online for two months. Produced with support from: TOTAL |
|
 |
| |
Thesis |  Top Top |
 |
 |
 |
Homemade chemists p687
Michelle Francl
doi:10.1038/nchem.1441
Michelle Francl wonders if home labs make (better) chemists.
|
 |
Research Highlights |  Top Top |
 |
 |
 |
Molecular machines: Intracrystalline inflation | Cluster chemistry: Filling in the blanks | 'On water' chemistry: Interfacial understanding | Polymer chemistry: Alive with light
|
Blogroll |  Top Top |
 |
 |
 |
Blogroll: But is it art? p691
See Arr Oh
doi:10.1038/nchem.1440
|
 |
News and Views |  Top Top |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
Perspective |  Top Top |
 |
 |
 |
Design strategies for organic semiconductors beyond the molecular formula pp699 - 704
Zachary B. Henson, Klaus Müllen and Guillermo C. Bazan
doi:10.1038/nchem.1422
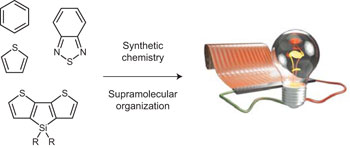
Although the molecular formula gives valuable information on the properties of isolated molecules or conjugated polymers, it fails to accurately predict their collective behaviour in the solid state. This Perspective highlights the importance of organization across multiple length scales on the optical and electronic properties of organic semiconductors, and how device performances poorly reflect the capabilities of a given material.
|
 |
Articles |  Top Top |
 |
 |
 |
Designed, synthetically accessible bryostatin analogues potently induce activation of latent HIV reservoirs in vitro pp705 - 710
Brian A. DeChristopher, Brian A. Loy, Matthew D. Marsden, Adam J. Schrier, Jerome A. Zack and Paul A. Wender
doi:10.1038/nchem.1395
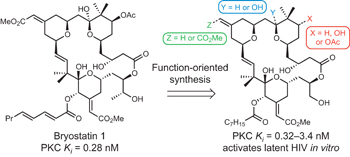
Simplified bryostatin analogues are shown to potently induce latent HIV expression in vitro. These analogues display comparable or better potency when compared with bryostatin. Moreover, they are up to 1,000-fold more potent in inducing latent HIV expression than prostratin, the current lead preclinical candidate.
Chemical compounds
See also: News and Views by Melander & Margolis
|
 |
 |
 |
Key stabilizing elements of protein structure identified through pressure and temperature perturbation of its hydrogen bond network pp711 - 717
Lydia Nisius and Stephan Grzesiek
doi:10.1038/nchem.1396
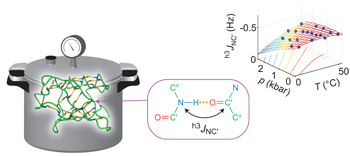
The pressure- and temperature-dependent changes of various hydrogen bonds within ubiquitin have been determined at very high resolution using NMR H-bond scalar couplings. The measured perturbations show a correlation with the sequence separation between donor and acceptor residues, and indicate that certain topologically crucial H-bonds are specifically stabilized.
See also: News and Views by Nielsen & Schwalbe
|
 |
 |
 |
A simple and accessible synthetic lectin for glucose recognition and sensing pp718 - 723
Chenfeng Ke, Harry Destecroix, Matthew P. Crump and Anthony P. Davis
doi:10.1038/nchem.1409
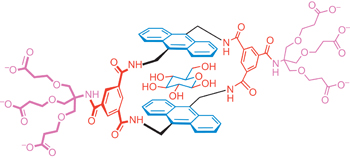
Selective carbohydrate binding is a difficult task, usually accomplished by proteins (lectins) or complex synthetic analogues. It has now been achieved by a remarkably simple compound, accessible in just five steps from commercially available materials. This new receptor is highly selective for all-equatorial carbohydrates, and may be used to sense glucose through changes in anthracene fluorescence.
Chemical compounds
See also: News and Views by Kubik
|
 |
 |
 |
Understanding and controlling the substrate effect on graphene electron-transfer chemistry via reactivity imprint lithography pp724 - 732
Qing Hua Wang, Zhong Jin, Ki Kang Kim, Andrew J. Hilmer, Geraldine L. C. Paulus, Chih-Jen Shih, Moon-Ho Ham, Javier D. Sanchez-Yamagishi, Kenji Watanabe, Takashi Taniguchi, Jing Kong, Pablo Jarillo-Herrero and Michael S. Strano
doi:10.1038/nchem.1421
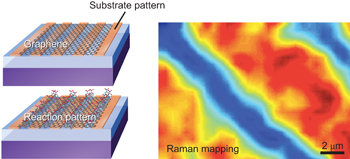
The chemical modification of graphene is important for its use in many applications. Now it is shown that the reactivity of graphene towards covalent modification varies widely depending on its underlying support substrate, and that the substrate can be patterned to induce spatial control of chemical reactions in graphene.
|
 |
 |
 |
Highly enantioselective trapping of zwitterionic intermediates by imines pp733 - 738
Huang Qiu, Ming Li, Li-Qin Jiang, Feng-Ping Lv, Li Zan, Chang-Wei Zhai, Michael P. Doyle and Wen-Hao Hu
doi:10.1038/nchem.1406
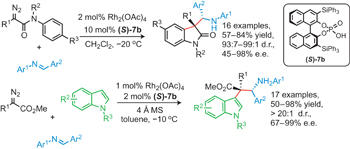
Reactions with unstable and highly reactive zwitterionic intermediates generated in transition-metal-catalysed processes provide new opportunities for molecular constructions. Here imines, activated by chiral organocatalysts, have been employed to trap the zwitterionic intermediates to give polyfunctionalized indole and oxindole derivatives in a single step with excellent diastereoselectivity and enantioselectivity.
Chemical compounds
|
 |
 |
 |
In situ surface coverage analysis of RuO2-catalysed HCl oxidation reveals the entropic origin of compensation in heterogeneous catalysis pp739 - 745
Detre Teschner, Gerard Novell-Leruth, Ramzi Farra, Axel Knop-Gericke, Robert Schlögl, László Szentmiklósi, Miguel González Hevia, Hary Soerijanto, Reinhard Schomäcker, Javier Pérez-Ramírez and Núria López
doi:10.1038/nchem.1411
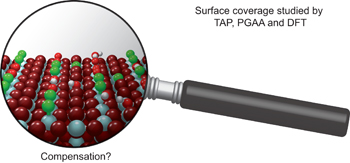
In heterogeneous catalytic processes the Arrhenius parameters are often found to be interrelated (compensation phenomenon). Using state-of-the-art experiments and density functional theory, the origin of compensation is studied. A similar dependence on the rate-limiting surface-coverage term is found for both apparent activation energy and prefactor terms, which can be translated into surface configurational entropy contributions.
|
 |
 |
 |
A quantitative model for the transcription of 2D patterns into functional 3D architectures pp746 - 750
Edvinas Orentas, Marco Lista, Nai-Ti Lin, Naomi Sakai and Stefan Matile
doi:10.1038/nchem.1429
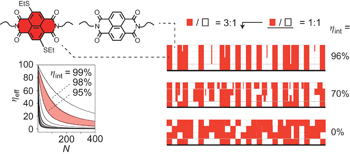
The self-sorting of molecular building blocks should allow 2D surface patterns to be transcribed into 3D functional materials. Here, a non-empirical approach to the templated synthesis of supramolecular architectures on surfaces is reported, starting with a theoretical model and followed by comprehensive experimental validation, including direct evidence for functional relevance of the produced materials.
Chemical compounds
|
 |
 |
 |
Anion-induced reconstitution of a self-assembling system to express a chloride-binding Co10L15 pentagonal prism pp751 - 756
Imogen A. Riddell, Maarten M. J. Smulders, Jack K. Clegg, Yana R. Hristova, Boris Breiner, John D. Thoburn and Jonathan R. Nitschke
doi:10.1038/nchem.1407
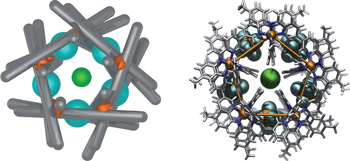
A coordination cage has been prepared that self-assembles through second-order templation. Peripheral perchlorate or hexafluorophosphate template anions direct the formation of a hollow prism whose central pocket was able to bind a small anionic guest such as halide or azide, in a manner reminiscent to signal transduction in biological systems.
|
 |
 |
 |
A switching cascade of hydrazone-based rotary switches through coordination-coupled proton relays pp757 - 762
Debdas Ray, Justin T. Foy, Russell P. Hughes and Ivan Aprahamian
doi:10.1038/nchem.1408
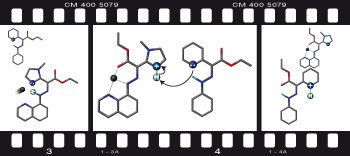
Metal cations play an important role in biological proton relays by modulating the pKa values of surrounding amino acids. This effect has now been used to induce the isomerization of two hydrazone switches using a single input. It is found that a combination of electrostatic repulsion and conformational changes are required for the proton relay to take place.
Chemical compounds
See also: News and Views by Burdette
|
 |
In Your Element |  Top Top |
 |
 |
 |
Reactions coupled to palladium p764
Matthew Hartings
doi:10.1038/nchem.1437
You would be forgiven if you thought the most important element in an organic transformation was carbon. Matthew Hartings argues that, for just over half a century in many of chemistry's most renowned organic reactions, it has actually been palladium.
|
 |
 Top Top |
 |
 |
 |
| Advertisement |
 |
Nature Chemistry – New Impact Factor
The 2011 ISI impact factor for Nature Chemistry is 20.524*, according to the ISI Journal Citation Reports®. This places Nature Chemistry first among all primary research journals in chemistry.
*2011 Journal Citation Reports® (Thomson Reuters, 2012) |
|
 |
| |
 |  |  |  |  |  | Natureevents is a fully searchable, multi-disciplinary database designed to maximise exposure for events organisers. The contents of the Natureevents Directory are now live. The digital version is available here.
Find the latest scientific conferences, courses, meetings and symposia on natureevents.com. For event advertising opportunities across the Nature Publishing Group portfolio please contact natureevents@nature.com |  |  |  |  |  |
|
 |


No comments:
Post a Comment