Dear Reader ,
Here is your customized Science X Newsletter for week 26:
 | Cannabinoids remove plaque-forming Alzheimer's proteins from brain cellsSalk Institute scientists have found preliminary evidence that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and other compounds found in marijuana can promote the cellular removal of amyloid beta, a toxic protein associated with Alzheimer's disease. |
 | Scientists find 'water windfall' beneath California's Central ValleyCalifornia's drought-stricken Central Valley harbors three times more groundwater than previously estimated, Stanford scientists have found. Accessing this water in an economically feasible way and safeguarding it from possible contamination from oil and gas activities, however, will be challenging. |
 | Beyond video games: New artificial intelligence beats tactical experts in combat simulationArtificial intelligence (AI) developed by a University of Cincinnati doctoral graduate was recently assessed by subject-matter expert and retired United States Air Force Colonel Gene Lee - who holds extensive aerial combat experience as an instructor and Air Battle Manager with considerable fighter aircraft expertise - in a high-fidelity air combat simulator. |
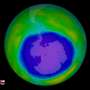 | Scientists observe first signs of healing in the Antarctic ozone layerScientists at MIT and elsewhere have identified the "first fingerprints of healing" of the Antarctic ozone layer, published today in the journal Science. |
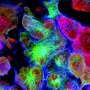 | Researcher develops new, non-invasive method to wipe out cancerous tumorsMatthew Gdovin, an associate professor in the UTSA Department of Biology, has developed a newly patented method to kill cancer cells. His discovery, described in a new study in The Journal of Clinical Oncology, may tremendously help people with inoperable or hard-to-reach tumors, as well as young children stricken with cancer. |
 | Huge helium discovery 'a life-saving find'A new approach to gas exploration has discovered a huge helium gas field, which could address the increasingly critical shortage of this vital yet rare element. |
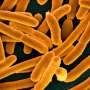 | Indicator of chronic fatigue syndrome found in gut bacteriaPhysicians have been mystified by chronic fatigue syndrome, a condition where normal exertion leads to debilitating fatigue that isn't alleviated by rest. There are no known triggers, and diagnosis requires lengthy tests administered by an expert. |
 | Micro-camera can be injected with a syringeGerman engineers have created a camera no bigger than a grain of salt that could change the future of health imaging—and clandestine surveillance. |
 | No association between 'bad cholesterol' and elderly deaths, new study saysA University of South Florida professor and an international team of experts have found that older people with high levels of a certain type of cholesterol, known as low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C), live as long, and often longer, than their peers with low levels of this same cholesterol. |
 | Juno peers inside a giantNASA's Juno spacecraft will make its long anticipated arrival at Jupiter on July 4. Coming face-to-face with the gas giant, Juno will begin to unravel some of the greatest mysteries surrounding our solar system's largest planet, including the origin of its massive magnetosphere. |
 | Researchers identify calorie-burning pathway in fat cellsInvestigators at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in collaboration with scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, have identified a natural molecular pathway that enables cells to burn off calories as heat rather than store them as fat. This raises the possibility of a new approach to treating and preventing obesity, diabetes, and other obesity-linked metabolic disorders including cancer. |
 | Juno spacecraft getting close to JupiterNASA's Juno mission, launched nearly five years ago, will soon reach its final destination: the most massive planet in our solar system, Jupiter. On the evening of July 4, at roughly 9 p.m. PDT (12 a.m. EDT, July 5), the spacecraft will complete a burn of its main engine, placing it in orbit around the king of planets. |
 | Astronomers release spectacular survey of the distant UniverseAstronomers today (28 June) released spectacular new infrared images of the distant Universe, providing the deepest view ever obtained over a large area of sky. The team, led by Prof Omar Almaini, present their results at the National Astronomy Meeting at the University of Nottingham. |
 | Little to no association between butter consumption and chronic disease or total mortalityButter consumption was only weakly associated with total mortality, not associated with cardiovascular disease, and slightly inversely associated (protective) with diabetes, according to a new epidemiological study which analyzed the association of butter consumption with chronic disease and all-cause mortality. This systematic review and meta-analysis, published in PLOS ONE, was led by Tufts scientists including Laura Pimpin, Ph.D., former postdoctoral fellow at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts in Boston, and senior author Dariush Mozaffarian, M.D., Dr.P.H., dean of the School. |
 | Team discovers moon over Makemake in the Kuiper BeltA Southwest Research Institute-led team has discovered an elusive, dark moon orbiting Makemake, one of the "big four" dwarf planets populating the Kuiper Belt region at the edge of our solar system. The findings are detailed in the paper "Discovery of a Makemakean Moon," published in the June 27 issue of Astrophysical Journal Letters. |
 | Hubble reveals stellar fireworks in 'skyrocket' galaxyFireworks shows are not just confined to Earth's skies. NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. |
 | Turn your smartphone into any kind of sensorIt started when NASA answered a call for a tool to detect dangerous gases and chemicals with a smartphone. The result became a smartphone-linked device that can do, well, just about anything someone can build a sensor for. |
 | Seeds of black holes could be revealed by gravitational waves detected in spaceScientists led by Durham University's Institute for Computational Cosmology ran the huge cosmological simulations that can be used to predict the rate at which gravitational waves caused by collisions between the monster black holes might be detected. |
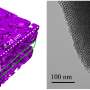 | New biomaterial developed for injectable neuronal controlIn the campy 1966 science fiction movie "Fantastic Voyage," scientists miniaturize a submarine with themselves inside and travel through the body of a colleague to break up a potentially fatal blood clot. Right. Micro-humans aside, imagine the inflammation that metal sub would cause. |
 | Laser pulses produce glowing plasma filaments in open air, could enable long-distance monitoringResearchers at MIT and elsewhere have found a new way of using mid-infrared lasers to turn regions of molecules in the open air into glowing filaments of electrically charged gas, or plasma. The new method could make it possible to carry out remote environmental monitoring to detect a wide range of chemicals with high sensitivity. |
This email is a free service of Science X Network
You received this email because you subscribed to our list.
If you no longer want to receive this email use the link below to unsubscribe.
https://sciencex.com/profile/nwletter/
You are subscribed as jmabs1@gmail.com
No comments:
Post a Comment