Dear Reader ,
Here is your customized Science X Newsletter for week 24:
 | Olli, a 3D printed, self-driving minibus, to hit the road in USA new maker of self-driving vehicles burst onto the scene Thursday in partnership with IBM's supercomputer platform Watson, and it's ready to roll right now. |
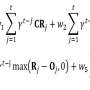 | Happiness equation: New equation reveals how other people's fortunes affect our happinessA new equation, showing how our happiness depends not only on what happens to us but also how this compares to other people, has been developed by UCL researchers funded by Wellcome. |
 | Life's first handshake: Chiral molecule detected in interstellar spaceLike a pair of human hands, certain organic molecules have mirror-image versions of themselves, a chemical property known as chirality. These so-called "handed" molecules are essential for biology and have intriguingly been found in meteorites on Earth and comets in our Solar System. None, however, has been detected in the vast reaches of interstellar space, until now. |
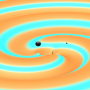 | Gravitational waves detected from second pair of colliding black holesOn December 26, 2015 at 03:38:53 UTC, scientists observed gravitational waves—ripples in the fabric of spacetime—for the second time. |
 | Unknown alien rock found in Swedish quarryA morsel of never-before-seen alien rock has been dug up in a limestone quarry in Sweden, where it had lain deeply buried for about 470 million years, scientists said Tuesday. |
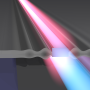 | Scientists amplify light using sound on a silicon chipYale scientists have found a way to greatly boost the intensity of light waves on a silicon microchip using the power of sound. |
 | Physicists measured something new in the radioactive decay of neutronsA physics experiment performed at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has enhanced scientists' understanding of how free neutrons decay into other particles. The work provides the first measurement of the energy spectrum of photons, or particles of light, that are released in the otherwise extensively measured process known as neutron beta decay. The details of this decay process are important because, for example, they help to explain the observed amounts of hydrogen and other light atoms created just after the Big Bang. |
 | New imaging method reveals nanoscale details about DNAResearchers have developed a new enhanced DNA imaging technique that can probe the structure of individual DNA strands at the nanoscale. Since DNA is at the root of many disease processes, the technique could help scientists gain important insights into what goes wrong when DNA becomes damaged or when other cellular processes affect gene expression. |
 | Did gravitational wave detector find dark matter?When an astronomical observatory detected two black holes colliding in deep space, scientists celebrated confirmation of Einstein's prediction of gravitational waves. A team of astrophysicists wondered something else: Had the experiment found the "dark matter" that makes up most of the mass of the universe? |
 | 3-D printed polymer turns methane to methanolLawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists have combined biology and 3-D printing to create the first reactor that can continuously produce methanol from methane at room temperature and pressure. |
 | Scientists detect most distant signs of oxygen in the universeAstronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) detected a clear signal from oxygen in a galaxy located 13.1 billion light-years away from us. This is the most distant oxygen ever detected. Oxygen in this galaxy seems to be ionized by a number of young giant stars, and this detection is a key step to understand the enigmatic "cosmic reionization" in the early history of the Universe. These observations have opened a new window to probe the early Universe with ALMA. |
 | Relax, it'll be 1,500 years before aliens contact usIf you're expecting to hear from aliens from across the universe, it could be a while. |
 | Kepler-1647b: New planet is largest discovered that orbits two sunsIf you cast your eyes toward the constellation Cygnus, you'll be looking in the direction of the largest planet yet discovered around a double-star system. It's too faint to see with the naked eye, but a team led by astronomers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center and San Diego State University used the Kepler Space Telescope to identify the new planet, Kepler-1647b. The discovery was announced today in San Diego, at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society. |
 | World's first 1,000-processor chipA microchip containing 1,000 independent programmable processors has been designed by a team at the University of California, Davis, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The energy-efficient "KiloCore" chip has a maximum computation rate of 1.78 trillion instructions per second and contains 621 million transistors. The KiloCore was presented at the 2016 Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits in Honolulu on June 16. |
 | Physicists observe behavior of quantum materials in curved spaceLight and matter are typically viewed as distinct entities that follow their own, unique rules. Matter has mass and typically exhibits interactions with other matter, while light is massless and does not interact with itself. Yet, wave-particle duality tells us that matter and light both act sometimes like particles, and sometimes like waves. |
 | Cats seem to grasp the laws of physicsCats understand the principle of cause and effect as well as some elements of physics. Combining these abilities with their keen sense of hearing, they can predict where possible prey hides. These are the findings of researchers from Kyoto University in Japan, led by Saho Takagi and published in Springer's journal Animal Cognition. |
 | Very hot drinks 'probably' cause cancer: UN agency (Update)Very hot drinks probably increase the risk of cancer, a UN agency said Wednesday, but coffee—once feared to be a carcinogen—is safe if enjoyed at "normal" temperatures. |
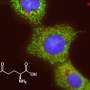 | Starving cancer cells by blocking their metabolismScientists at EPFL have found a way to starve liver cancer cells by blocking a protein that is required for glutamine breakdown—while leaving normal cells intact. The discovery opens new ways to treat liver cancer. |
 | Researchers find new ways to make clean hydrogen and rechargable zinc batteriesA Stanford University research lab has developed new technologies to tackle two of the world's biggest energy challenges - clean fuel for transportation and grid-scale energy storage. |
 | New lizard found in Dominican RepublicA University of Toronto-led team has reported the discovery of a new lizard in the middle of the most- visited island in the Caribbean, strengthening a long-held theory that communities of lizards can evolve almost identically on separate islands. |
This email is a free service of Science X Network
You received this email because you subscribed to our list.
If you no longer want to receive this email use the link below to unsubscribe.
https://sciencex.com/profile/nwletter/
You are subscribed as jmabs1@gmail.com
No comments:
Post a Comment